Ever wondered where the UAE ends and its neighbors begin? The United Arab Emirates, a Gulf country of seven Emirates, has a unique geography. It’s as fascinating as its rapid development. Nestled in the eastern Arabian Peninsula, this nation of 9.9 million people is small but mighty.
It covers just 83,600 square kilometers. But what defines the UAE’s national borders? And how does its boundary overview shape its role in the region?
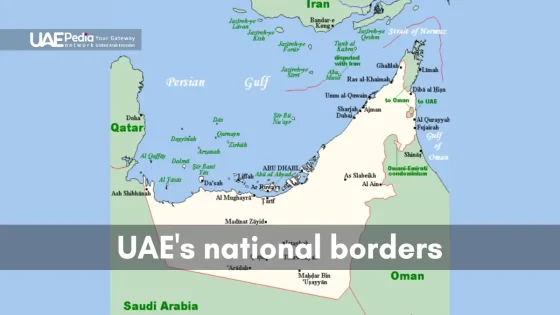
From Dubai’s bustling cityscapes to Jabal Bil ‘Ays’ rugged peaks, the UAE’s border geography is full of contrasts. It shares 1,066 km of land boundaries with Oman and Saudi Arabia. Plus, it has a 1,318 km coastline along the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman.
The Emirates sit at a crossroads of global trade and cultural exchange. Let’s explore how these borders have shaped one of the world’s most dynamic nations.
Historical Evolution of UAE Border Formation
The United Arab Emirates’ borders have a rich history. They started in the Trucial States era. This time shaped the UAE’s current borders in West Asia.
It changed the UAE from a British protectorate to an independent nation in the Middle East.
British Protectorate Period (1820-1971)
In 1820, the British signed peace treaties with local tribes Defining. This created the Trucial States. The goal was to secure trade routes and keep the region stable.
The Nahyan dynasty of Abu Dhabi became very powerful. They played a big role in the UAE’s future.
Post-Independence Border Establishment
The UAE became independent in 1971. This started a new era of border treaties and agreements. At first, it had six emirates.
Ras Al Khaimah joined in 1972, making the federation complete. This time was filled with talks with neighboring countries to set the UAE’s borders.
Trucial States to Modern Federation
The move from Trucial States to a modern federation was complex. UAE border agreements were key in setting its 83,600 km² territory. These agreements show the UAE’s growth from separate emirates to a unified country in the Middle East.
| Period | Key Events | Impact on Borders |
|---|---|---|
| 1820-1971 | British Protectorate Era | Establishment of Trucial States |
| 1971 | UAE Independence | Formation of initial federation |
| 1972 | Ras Al Khaimah Joins | Completion of current UAE borders |
UAE National Borders and Geographic Position
The United Arab Emirates is in a great spot on the Arabian Peninsula. It has different lands, like sandy deserts and rocky mountains. Its place by the Persian Gulf is key for its economy and politics.
Strategic Location in the Arabian Peninsula
The UAE’s spot on the Arabian Peninsula is very good. It shares borders with Saudi Arabia and Oman. Its coast is by the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. This spot has helped shape its history, trade, and world relations.
Total Land Area and Border Length
The UAE is a bit smaller than Portugal, with 83,600 square kilometers. Its borders are about 1,066 kilometers long. The border with Saudi Arabia is on the west and south. Oman is on the east and northeast.
| Neighboring Nation | Border Length (km) |
|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | 457 |
| Oman | 609 |
Key Border Crossing Points
There are important border crossings between the UAE and its neighbors. Some key ones are:
- Al Ghuwaifat: Links the UAE with Saudi Arabia
- Al Ain/Buraimi: Connects the UAE to Oman
- Hatta: Another crossing point with Oman
These crossings are important for trade, tourism, and sharing cultures between the UAE and its neighbors.
Maritime Boundaries and Coastal Territories
The UAE’s maritime borders stretch along Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman. This is a key part of the nation’s geography. It plays a big role in the country’s economy and strategy.
Persian Gulf Coastline
The UAE’s Persian Gulf coastline is very active. Abu Dhabi, the biggest emirate, has a 280-mile shoreline. This area has big oil reserves, with the first oil discovery in 1958.
Gulf of Oman Maritime Border
The UAE’s eastern coast looks out onto the Gulf of Oman. This border gives the UAE a strategic edge in global trade. It adds to the UAE’s coastal variety.
Strategic Maritime Points and Ports
UAE ports are crucial for the nation’s maritime power. Jebel Ali in Dubai is one of the biggest man-made harbors. The UAE’s ports help it be a global trade center and boost its economy.
| Maritime Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Coastline Length | 1,318 km |
| Key Ports | Jebel Ali (Dubai), Khalifa Port (Abu Dhabi) |
| Strategic Point | Strait of Hormuz |
| Economic Significance | Oil exports, international trade |
Neighboring Countries and Border Relations
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has borders with several countries. Saudi Arabia and Oman are its land neighbors. Iran and Qatar share the sea border with the UAE. These countries are important for the UAE’s economy and politics.
The UAE has had some border issues in the past. For example, it solved a problem with Saudi Arabia over oil in 1974. It also worked with Iran to fix sea border issues, showing it wants peace.
The UAE aims to keep the region stable and grow its economy. It’s part of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). By using diplomacy and arbitration, the UAE has managed its borders well. This makes it a key player in the Arabian Peninsula.