What if sand could sprout tomatoes? Since 1971, crop production here has grown 1,300% – a testament to human ingenuity where summer temperatures regularly hit 122°F. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality for those coaxing life from arid soil.
From Al Ain’s ancient falaj irrigation to Ras Al Khaimah’s vertical farms, growers blend tradition with tech. Sheikh Zayed’s vision of “greening the desert” now meets AI-driven hydroponics and solar-powered cooling. Yet every triumph faces hurdles: 80% of water comes from desalination plants, and shifting weather patterns demand constant adaptation.
We’ll walk through date palm groves and climate-controlled domes, exploring how:
- Legacy techniques meet drone monitoring systems
- Scarce rainfall sparks creative water solutions
- Global shifts affect local harvests and food security
Pack your virtual iced karak chai – let’s explore how desert cultivators rewrite the rules of nature.
Understanding the Evolution of UAE Agriculture
How did date palms become the original influencers of desert cultivation? Long before drones monitored crops, ancestors in Liwa Oasis tapped into nature’s rhythm. They engineered falaj channels—gravity-fed waterways—to turn sand into sustenance. These underground veins transformed arid plots into thriving date farms, proving even harsh landscapes could yield life.
Historical Roots and Early Practices
Walk through Al Ain’s palm groves, and you’ll spot 3,000-year-old irrigation blueprints. Farmers here mastered crop rotation, using salt-tolerant barley to prep soil for sweeter fruits. In Ras Al Khaimah, they bartered dried fish for seeds—early proof that scarcity breeds creativity. Water wasn’t just a resource; it was community currency, guarded like treasure.
Modern Developments Since 1971
Post-independence, the nation swapped camels for cucumbers in a bold agricultural pivot. Sheikh Zayed’s famous decree—“Give me agriculture, and I’ll give you civilization”—sparked a green revolution. Solar-powered hydroponics replaced mud-brick wells, while vertical farms now stretch toward skyscrapers. Today, 72% of the country’s tomatoes grow in climate-controlled domes, a delicious paradox in desert development.
From hand-dug channels to AI-driven drip systems, this journey mirrors humanity’s dance with nature. Next time you bite into a locally grown strawberry, remember: it’s not just fruit—it’s a 5,000-year-old story of grit and growth.
Navigating the UAE’s Unique Climate Challenges
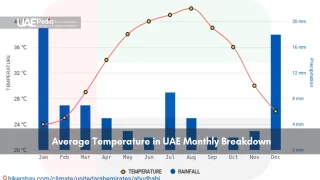
Imagine farming where summer nights feel like open ovens—heat lingering like uninvited guests. Daytime highs here could fry an egg on sandstone, while annual rainfall barely fills a teacup. Yet beneath this harsh ballet of elements, growers choreograph survival through smart water use and climate defiance.
Extreme Weather and Water Scarcity
Rain here plays hide-and-seek—some years bringing flash floods, others leaving cracked earth. Underground reserves shrink faster than mirages, pushing innovators to rethink every drop. Farmers now deploy moisture sensors that text alerts when crops thirst, slashing waste by 40% compared to flood irrigation.
Look closer: solar-powered hydroponic towers grow greens using 90% less liquid than soil farming. Drip systems borrowed from Israel’s Negev Desert now hydrate date palms in Abu Dhabi. “Every liter counts double,” says a Ministry report, noting 70% of freshwater goes to crops under the National Food Security Strategy 2051.
These aren’t just gadgets—they’re lifelines. As climate shifts redraw growing seasons, traditional knowledge meets AI forecasting. Sensors track soil salinity; drones map evaporation rates. Even camels get smart collars to prevent overgrazing. The desert still dictates terms, but cultivators answer with sharper tools.
Tomorrow’s solutions? Think fog-harvesting nets and salt-tolerant quinoa. For now, watch how sand becomes strategy—one innovation at a time.
Impact of Climate Change on Regional Agriculture
What if the desert’s breath could fuel a green revolution? Across the Gulf, growers face a new reality: 1.5°C hotter summers by 2030 (per updated NDC targets) and rainfall patterns that swing from drought to deluge. Yet this isn’t a dirge—it’s a drumbeat for smarter production methods reshaping the sector.
Rising Temperatures and Erratic Rainfall
Fields now endure heat spikes that wilt tomatoes in hours. Last year’s date harvest saw 12% smaller yields—not from pests, but relentless sun. “Our grandfathers tracked stars for rain clues,” says Emirati agronomist Fatima Al-Mansoori. “Now we use AI models predicting storms 72 hours out.”
Unpredictable downpours challenge even tech-savvy farms. Sensors detect soil moisture shifts, while drought-resistant quinoa varieties thrive where barley once struggled. The national strategy aims to slash water use per crop unit by 15% before 2030—a race against evaporation rates climbing 3% annually.
Air Quality and SLCP Emissions
Dust storms aren’t just gritty nuisances—they carry pollutants affecting both crops and communities. The nation’s 120 air monitoring stations feed real-time data into farming apps, helping time planting cycles around particulate levels.
COP26 commitments accelerated SLCP reductions: methane from compost sites now fuels bioenergy plants, cutting emissions by 23% since 2021. A Ministry of Climate Change report notes, “Every ton of CO2 we prevent means 40kg of preserved grain yield—that’s security you can taste.”
From solar-powered desalination to carbon-capturing greenhouses, challenges spark smarter solutions. As global temps rise, so does regional resolve—turning climatic hurdles into launchpads for innovation.
Modern Farming Technology and Irrigation Innovations
Picture a farm where roots dangle in air, nourished by nutrient-rich mist instead of soil. This isn’t sci-fi—it’s hydroponics in action, turning scarcity into abundance. Growers now harness tech to squeeze every drop from precious resources, blending ancient wisdom with tomorrow’s tools.
Roots in the Sky
Sharjah’s vertical wheat project grows 18x more grain per liter than conventional fields. “We’re farming upward, not outward,” explains lead agronomist Amal Khalid. Her team uses 95% less water by cycling mist through stacked trays—a technique borrowed from Singapore’s sky farms.
Smart Water Ballet
Compare old and new:
| Method | Water Use | Crop Yield | Tech Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flood Irrigation | 1,000 L/day | Medium | Low |
| Drip Systems | 220 L/day | High | Medium |
| Hydroponics | 90 L/day | Very High | High |
The Ministry of Climate Change backs these shifts through grants for solar-powered drip tech. One Al Dhaid melon farm cut water waste by 78% while doubling harvests—proof that sustainable agriculture pays dividends.
Farmers aren’t just adopting gadgets—they’re rethinking entire food systems. Sensor networks predict plant thirst before leaves wilt. Saltwater-cooled greenhouses grow strawberries in summer. Each innovation stitches into the national vision for resilient harvests.
As one grower told me: “Our grandfathers prayed for rain. We engineer it.” From fog nets to AI irrigation, the desert’s future blooms with clever solutions.
Agricultural Food Systems and Sustainable Production
How do you build a buffet in a land of dunes? The answer lies in networks smarter than any oasis—food systems connecting vertical farms to markets, solar-powered logistics to your plate. Growers here don’t just produce crops—they engineer ecosystems where scarcity becomes abundance.
Integrated networks now supply 42% of fresh produce to local supermarkets, up from 18% in 2010. Blockchain tracks lettuce from Sharjah’s hydroponic towers to Dubai salad bars in 90 minutes flat. “We’re designing circular systems,” notes an ESMA organic certification officer. “Compost from Abu Dhabi date farms feeds Al Ain tomato seedlings—zero waste, maximum flavor.”
Challenges spark creative fixes. Salt-tolerant quinoa thrives in recycled aquaculture water. Solar desalination plants pipe clean water to 160+ greenhouse clusters. The National Food Security Strategy 2051 aims for 50% self-sufficiency in key crops—without draining aquifers.
Three shifts redefine sustainability here:
- AI predicts supermarket demand to reduce overproduction
- Urban rooftop gardens yield 8x more herbs per square meter
- Lab-grown camel milk slashes methane emissions by 64%
Government grants fast-track innovations like these. One Fujairah project combines wind towers and ancient cooling techniques to store vegetables without electricity. Another in Ajban uses drones to pollinate 10,000 saffron flowers per hour.
This isn’t just farming—it’s a culinary revolution rewriting the rules of possibility. Next time you bite into a crisp local cucumber, taste the grit and genius behind every crunch.
Government Initiatives and Strategic Policies
Ever seen a desert bloom with policy papers? The nation recently launched its most ambitious farming revolution yet—not with seeds, but strategic blueprints. Through climate diplomacy efforts like the COP28 Action Agenda, leaders are rewriting the rules of arid cultivation.
Abu Dhabi spearheads this shift. Its Agriculture & Food Safety Authority rolled out 14 smart subsidies in 2023, slashing water use by 37% on participating farms. One standout initiative pairs solar-powered desalination plants with AI irrigation grids—think of it as a tech tango between tradition and innovation.
Three game-changing commitments shape progress:
- NDC targets now fund 80% of vertical farm startups
- Food Security Strategy 2051 mandates 30% organic waste recycling by 2027
- Farm-to-fork blockchain tracking ensures safety from soil to supermarket
Support comes in unexpected forms. A Ras Al Khaimah grower shared: “They gave us weather-controlled greenhouses that pay for themselves in two harvests.” That’s not hyperbole—it’s the outcome of Vision 2021’s $270 million agri-tech fund.
You’ll find smart subsidies for drone pollination kits in Al Ain and R&D grants for salt-tolerant crops in Fujairah. As one official noted, “We’re not just growing tomatoes—we’re cultivating resilience.” With every policy paper and public-private pact, the sands shift toward a greener tomorrow.
Research, Innovation, and the Future of Farming
What if every seed carried a climate solution in its DNA? Labs now engineer drought-proof crops using AI-driven gene editing—think barley that thrives on seawater or tomatoes ripening under LED sunsets. This isn’t tomorrow’s fantasy; it’s today’s toolkit for reimagining cultivation.
AIM for Climate and Food Systems Transformation
The Agriculture Innovation Mission for Climate (AIM for Climate) cracks the code on food security. Backed by global partners, this $8 billion effort turbocharges projects like solar-powered pollination drones and soil microbes that capture carbon. “We’re not just adapting—we’re rewriting the rules,” says lead researcher Dr. Yasmin Al-Hamadi. Her team’s salt-tolerant wheat strains already boost yields by 18% in saline regions.
Three breakthroughs define this transition:
- Smart sensors predicting pest outbreaks 14 days early
- Vertical farms producing 200% more leafy greens per watt
- Blockchain platforms slashing food waste through real-time harvest tracking
Climate action fuels tangible wins. In Arizona, AIM-funded aquaponics systems now drip-feed deserts, while Kenyan herders use satellite apps to rotate grazing zones. These aren’t isolated experiments—they’re blueprints for a hungrier, hotter world.
Picture this: robotic bees pollinating orchards as bioengineered roots mine groundwater. Farmers once battling dust storms might soon trade weather apps for AI co-pilots. The future isn’t just coming—it’s sprouting in labs and test plots worldwide. Ready to taste what’s growing?
UAE climate and agriculture: Regional and Global Perspectives
Who thought a desert nation could host the world’s largest vertical farm summit? Last year’s Global Food Innovation Forum in Dubai drew 140 countries—proof that sand-grown solutions now shape planetary conversations. The Emirates doesn’t just adapt to scarcity; it exports blueprints for turning adversity into abundance.
Strategic alliances amplify this impact. Take the U.S.-UAE Accelerating Food Security Partnership, channeling $13 billion into climate-smart tech across 15 nations. “We’re co-designing drought-resistant seeds for Ethiopian highlands using AI models tested here,” shares Mariam Al Mheiri, Minister of Climate Change. Her team recently showcased solar desalination systems at COP28 that could slash irrigation costs worldwide.
“Our farms are living labs—what works under 122°F heat becomes a toolkit for farmers from Arizona to Australia.”
Three ways these collaborations ripple outward:
- Joint ventures with MIT spin-offs creating portable hydroponic units for refugee camps
- Abu Dhabi’s $2 billion agri-tech fund backing vertical farming startups in Texas
- Blockchain platforms developed with IBM tracking carbon-neutral produce from desert to dinner plates
Meetings like the World Economic Forum’s special session on arid-region agriculture position the nation as both student and teacher. Investors now see sand not as a barrier, but as the ultimate testing ground for tomorrow’s food systems. From camel milk protein bars stocked in New York gyms to AI irrigation apps used in Chilean vineyards, the proof is in the (globally sourced) pudding.
Pack your virtual passport—this isn’t just about dates and dunes. It’s about how a small peninsula’s grit feeds the world’s imagination.
Economic Impacts and Investment in Agriculture
Money grows faster than wheat in this desert economy. Take Sharjah’s vertical wheat farm—it now yields 22 tons annually while powering its LED lights through solar partnerships. Investors pour $4.3 billion into food production tech annually, proving greenbacks and greens thrive together.
Public-Private Partnerships and Project Investments
ADNOC’s AI soil scanners boost crop yields by 31% on partnered farms. The table below shows how strategic cash flow reshapes land use:
| Initiative | Investment | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Desalination Plants | $890M | +40% vegetable output |
| Drone Pollination Networks | $120M | 18% faster fruiting |
| AI Pest Control Systems | $65M | -29% crop loss |
These ventures aren’t charity—they’re profit engines. One Abu Dhabi date cooperative saw 200% ROI after adopting moisture-sensing tech funded by Emirates Development Bank.
Cross-Border Collaborations with the US
Texas-based Growcentia recently teamed up with local farms to deploy biofertilizers that slash water needs by half. “Our Arizona solar grids now power Ras Al Khaimah’s tomato domes,” shares MIT-trained engineer Layla Al Hashimi. Key joint ventures include:
- Portable hydroponic units for drought zones
- Blockchain platforms tracking carbon-neutral exports
- Gene-edited quinoa strains resisting 120°F heat
With 73% of agri-tech startups here attracting global funding, the sands shimmer with economic potential. As one investor quipped: “These crops don’t just feed stomachs—they feed portfolios.”
Opportunities and Challenges for Farmers in the UAE
Ever tasted a tomato grown in a sandstorm? Growers here juggle opportunities and obstacles like circus performers—balancing tech breakthroughs with a change environment that rewrites rules daily. Let’s unpack this high-stakes act.
Smart tools transform routines. Mobile apps now ping alerts when crops need water—like a plant whisperer in your pocket. Solar-powered drones map fields at dawn, spotting thirsty patches before human eyes can. “My grandfather carried a shovel,” says third-generation grower Fatima Al Remeithi. “I carry a tablet that tracks soil health from Dubai to Fujairah.”
Yet challenges multiply faster than desert wildflowers after rain. Erratic rainfall patterns force constant irrigation tweaks. Underground reservoirs drop 1.5 meters yearly. Market pressures push small farms to adopt pricey tech or risk fading like mirages.
| Challenge | Tech Solution | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Water scarcity | AI drip systems | 55% less waste |
| Soil salinity | Bioengineered crops | +22% yield |
| Labor costs | Harvesting robots | 40% faster |
Local efforts soften these blows. Training programs teach vertical farming techniques to 500+ growers annually. Grants cover 60% of solar panel costs for greenhouses. As climate shifts redraw the playbook, these efforts become lifelines—not luxuries.
Fatima’s farm tells the tale: she now grows mint in repurposed shipping containers using 90% less water. “We’re not just surviving the change environment,” she grins. “We’re writing new recipes for success.” From robot pollinators to salt-resistant seeds, tomorrow’s harvest looks bright—one innovation at a time.
Final Reflections on a Resilient Agricultural Future
What if tomorrow’s harvest began with yesterday’s wisdom? From ancient irrigation channels to AI-powered greenhouses, this journey reveals how systems evolve while honoring roots. Growers here don’t just adapt—they reimagine, blending solar tech with ancestral grit to turn scarcity into abundance.
Three lessons emerge. First: resilient systems thrive on collaboration. Government grants fuel vertical farms, while global partnerships export drought solutions worldwide. Second: innovation feeds sustainability. Hydroponic towers and smart sensors now yield more with less—water, land, and waste. Third: every challenge seeds opportunity. Salty soil births salt-tolerant crops; relentless sun powers solar desalination.
Your role? Stay curious. Explore how blockchain tracks produce from sandy soil to your plate. Share stories of robotic pollinators and fog-harvesting nets. These aren’t just local wins—they’re blueprints for a hungrier planet.
The future blooms where tradition meets transformation. As one farmer grinned while adjusting his drone: “Our ancestors planted dates. We’re growing possibilities.” Ready to dig deeper? The next chapter writes itself—with every seed sown and system refined.
The country invests in hydroponics, drip irrigation, and AI-powered systems to reduce water use by up to 90%. Projects like the Al Ain Vertical Farm showcase desert-grown crops using 95% less water than traditional methods.
Collaborations like the billion Agriculture Innovation Mission for Climate (AIM4C) with the US accelerate sustainable tech adoption. Emirates Bio Farm and Silal’s smart greenhouses exemplify how private ventures align with the National Food Security Strategy 2051.
Yes! Farms like Bustanica in Dubai—the world’s largest vertical farm—grow pesticide-free leafy greens using controlled environments. The Abu Dhabi Farmers’ Services Centre trains growers in regenerative practices to improve soil health despite arid conditions.
Rising temperatures stress pollination cycles, while soil salinity threatens yields. The UAE Date Palm Research Development Programme develops heat-tolerant varieties and sensor-based irrigation to protect this 7,000-year-old agricultural heritage.
The UAE’s Net Zero 2050 strategy supports solar-powered desalination plants and subsidies for agrivoltaic systems. The Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park powers vertical farms, cutting emissions while boosting tomato and strawberry production.
Cloud-seeding projects increase precipitation by 15-25%, while AI weather models from the National Centre of Meteorology help plan planting cycles. Wadi Showka’s terraced farms use ancient falaj systems redesigned with moisture sensors for efficient water distribution.