Contents
The UAE Coastal Geography is more critical to ships and trades along the Arabian Peninsula’s eastern coast, covering an area of approximately 83,600 km2 (approximately 32,300 miles). It shares borders with Saudi Arabia to the west and south, Oman to the east and southeast, and Iran to the north across the Persian Gulf (also known as the Arabian Gulf).
UAE Coastal Geography
The UAE has flat, desolate coastal plains. It meets the Arabian Gulf along its western coast, which has a coastline of more than 650 kilometers and is characterized by numerous inlets, or khors, and islands.
Tidal channels or sabkhas dominate Abu Dhabi’s coastal area, as do numerous islands such as Saadiyat Island, Yas Island, and SirBani Yas Island. The country has also built a significant number of man-made islands, particularly in the emirate of Dubai. The most well-known are the Palm Jumeirah, Palm Jebel Ali, and the World Islands, which were built for residential, leisure, and tourism purposes.
The eastern coastline of the Fujairah emirate, along the Gulf of Oman, is more rugged and mountainous, with a string of small bays and inlets. This coast has fewer islands, the most notable of which is Snoopy Island, a popular diving and snorkeling destination.
In contrast to its dry landscapes, the UAE has few permanent bodies of water. It has no notable rivers, and the only bodies of freshwater are artificial reservoirs and a few oases, such as Al Ain Oasis, which is fed by underground wells.
Read more: UAE Annual Precipitation
Geographical Regions of UAE
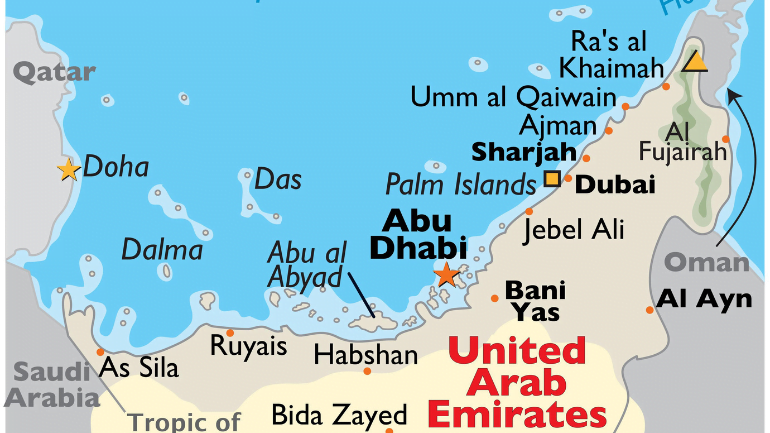
The UAE is divided into two major geographical regions and seven emirates. The majority of the area is made up of a desert hinterland with two major expanses of rolling sand dunes, the Rub Al Khali (The Empty Quarter) to the south and an area of gravel plains and dunes to the north of the Hajar mountains. Because of their arid and harsh environment, these areas are largely uninhabited and extend all the way to the barren coast.
Take a look at: Humidity Levels in UAE
Seas and Oceans
The northern and longest section of the UAE’s coastline is bordered by the Persian Gulf, with a short section to the east bordering the Gulf of Oman.
Seacoast & Undersea Features
Coral reefs can be found in shallow waters off the UAE’s eastern coast in the Gulf of Oman. The shoals are located off the UAE’s Persian Gulf coast, which lacks natural deepwater harbors in contrast to the Gulf of Oman coast, which has several.
Sea Straits and Inlets
The UAE is strategically located along the southern approaches to the Strait of Hormuz, which connects the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman and serves as a critical transit point for global crude oil shipments.
UAE Islands and Archipelagos
The UAE is made up of over a hundred islands, the majority of which are owned by Abu Dhabi. The country’s capital, Abu Dhabi, is located on the same-named island. Other islands, including Das Island, are used for oil and gas operations associated with offshore drilling.
Read more: Impact of Global Warming on UAE
The Emirates Map of the UAE
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), a federation in the Arabian Peninsula’s east, is made up of seven distinct emirates. Each emirate retains significant autonomy while participating in federal structures.
Abu Dhabi
The largest of the seven emirates, it spans 67,340 km (26,000 mi) and accounts for approximately 87% of the UAE’s total land area. It is home to the capital city of the same name, as well as the federal government of the UAE.
Dubai
The UAE’s economic hub, it is the second largest city after Abu Dhabi. It includes the famous city of Dubai, which is located on the southern shore of the Arabian Gulf and is one of the world’s most important financial and business centers.
Sharjah
Emirate Sharjah, which borders Dubai, has a long coastline on both the Arabian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. It also includes important enclaves such as Khor Fakkan, Kalba, and Dibba Al-Hisn.
Ajman
The UAE’s smallest emirate is located in the center of the country’s western coast. Despite its small size, it operates a significant port and has a free trade zone that attracts businesses from a variety of industries.
Umm Al Quwain
Umm Al Quwain is one of the less populated emirates, located just north of Ajman. Along its coast is a significant natural reserve, Al Seneyah Island.
Ras Al Khaimah
Located in the UAE’s northernmost region, it borders Oman’s exclave of Musandam. It has an important seaport and some of the most fertile agricultural land in the UAE.
Fujairah
Located on the UAE’s eastern coast along the Gulf of Oman, it is the country’s only access point to the Indian Ocean. The Port of Fujairah is a significant shipping port.
Take a look at: Extreme Weather Events in UAE
The United Arab Emirates in Atlas map
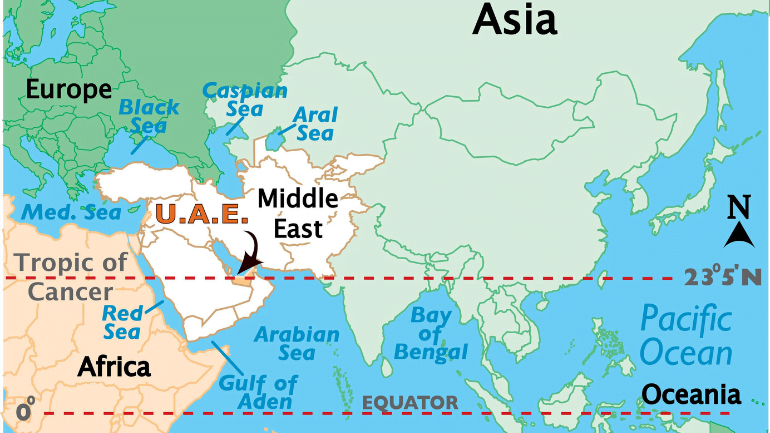
The United Arab Emirates is a Middle Eastern country located on the Arabian Peninsula’s northeastern edge, bordering the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf. It can be found in both the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres of the Earth. It is bounded on the south and west by Saudi Arabia, and on the east by Oman. Furthermore, it also has maritime borders with Iran to the north and Qatar to the west.
UAE Coastal Features
Six of the emirates have coasts on the Persian Gulf, while the seventh, Al Fujayrah, is located to the east along the Gulf of Oman. The Persian Gulf coast is dotted with islands, lagoons, and other indentations, and the shore is sandy with numerous salt flats (called sebkhas). The alluvial flats that border the Gulf of Oman on the eastern coast are an extension of the fertile coastal strip known as the Al Batinah coast, which runs between the mountains and the Sea of Oman.
Read more: UAE Weather Patterns
Why major cities in UAE are on the coast?
This is due to the UAE’s location in the Middle East and southwest Asia, where it borders the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman, between Oman and Saudi Arabia.
Which ocean covers UAE?
The UAE stretches for more than 650 kilometers (400 miles) along the Persian Gulf’s southern shore. The majority of the coast is made up of salt pans that extend far inland. According to a recent global remote sensing analysis, the United Arab Emirates has 637 km2 of tidal flats, ranking it 40th in terms of tidal flat extent. Dubai has the largest natural harbor, but other ports have been dredged in Abu Dhabi, Sharjah, and elsewhere.
What kind of geography does the UAE have?
The UAE is divided into three geographical zones: a flat, low-lying, barren coastal plain; rolling dunes stretching from the coast into a vast desert wasteland that blends into the Empty Quarter (Al-Rub al-Khali), the world’s largest sand desert; and a rugged mountain range shared with Oman.
Is Dubai a coastal desert?
That is correct, and it is sufficient to sustain a variety of small vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as desert plants like dwarf shrubs and grasses. Though Dubai is located on the Arabian Sea’s coast, it is also a harsh desert city that erupted directly from the Arabian Desert floor.
In the UAE Coastal Geography, there are no Inland lakes. Also, there are no lakes, rivers, or waterfalls There are no perennial rivers in the UAE. However, there are small areas of wetlands. Otherwise, all the UAE’s major ports are man-made, including Port Jabal Ali and Port Rashid, two of the Middle East’s largest artificial harbors. Irrigation canals support farming near Al Ayn’s Buraimi Oasis.













